Effective monitoring is crucial for maintaining system health and performance in today's complex software ecosystems. Two prominent approaches have emerged: OpenTelemetry and Application Performance Monitoring (APM). But which one is the better fit for your organization?
This article dives into the OpenTelemetry vs APM debate, highlighting the differences, strengths, and practical use cases to guide you in making the best choice.
What is OpenTelemetry and How Does it Differ from APM?
OpenTelemetry is an open-source observability framework designed to provide a standardised method of collecting and exporting telemetry data from applications and infrastructure. It creates a unified set of APIs, libraries, agents, and instrumentation to capture distributed traces, metrics, and logs across cloud-native, microservices-based environments.
On the other hand, APM (Application Performance Monitoring) is a more traditional monitoring solution focused on tracking and optimizing software performance, user experience, and business transactions. APM tools offer end-to-end visibility into the health and responsiveness of applications, often providing out-of-the-box monitoring solutions.
Why OpenTelemetry is Gaining Traction in the Monitoring Landscape
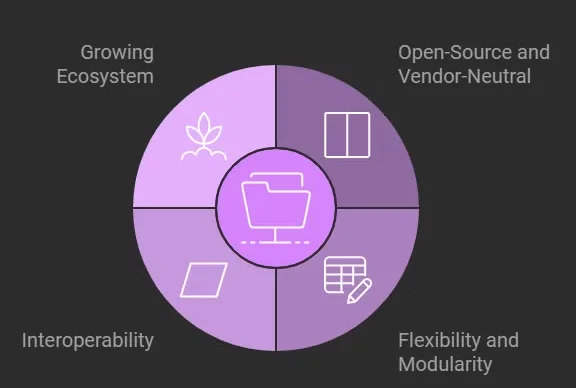
OpenTelemetry's popularity is growing rapidly, driven by several key factors:
- Open-Source and Vendor-Neutral: OpenTelemetry’s open-source, community-driven nature ensures organizations are not tied to any specific vendor, granting the flexibility to choose the most suitable tools and platforms for their unique requirements. This vendor-neutral approach promotes broader adoption and innovation.
- Flexibility and Modularity: OpenTelemetry’s modular design allows for seamless integration across diverse environments and systems, providing the freedom to customize data collection as per application needs. This flexibility ensures that it can be tailored to suit both simple and complex infrastructure.
- Interoperability: With a standardized data model, OpenTelemetry ensures compatibility across a wide range of observability platforms. This allows organizations to collect, process, and visualize telemetry data effortlessly, facilitating a unified view of system performance across different tools and ecosystems.
- Growing Ecosystem: OpenTelemetry’s rapidly growing community drives continuous innovation, ensuring timely support for modern architectures such as microservices and multi-cloud environments. This expansive ecosystem accelerates development and keeps pace with the latest trends in observability and performance monitoring.
How APM Solutions are Evolving in Response to OpenTelemetry
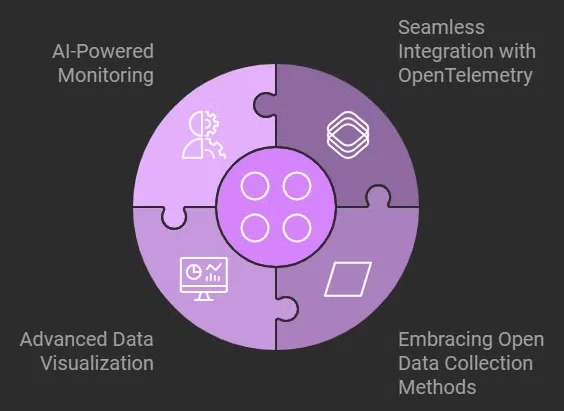
APM vendors are recognizing the advantages of OpenTelemetry and adapting to remain competitive. Here’s how they are responding:
- Seamless Integration with OpenTelemetry: Recognizing the growing influence of OpenTelemetry, many traditional APM vendors are adapting by offering built-in support for OpenTelemetry.
- This allows organizations to combine OpenTelemetry’s flexible telemetry data collection with the advanced analytics provided by APM tools, maximizing the strengths of both approaches.
- Embracing Open Data Collection Methods: To stay competitive, APM vendors are shifting toward more open and flexible data collection methodologies, aligning their capabilities with the flexibility that OpenTelemetry offers.
- This move enables organizations to gather data from a broader range of environments without being restricted to proprietary systems.
- Advanced Data Visualization: APM solutions are placing greater emphasis on their data analysis and visualization features, integrating cutting-edge tools such as machine learning and AI-driven insights.
- This helps users make sense of complex datasets and detect performance trends more effectively, offering a competitive edge in monitoring and troubleshooting.
- AI-Powered Monitoring: To improve proactive monitoring, APM vendors are increasingly embedding AI into their platforms.
- This enables predictive insights, allowing teams to identify potential performance issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime and optimizing system performance.
Comparing OpenTelemetry and APM: Key Considerations
When choosing between OpenTelemetry and APM, consider these critical factors:
| Aspect | OpenTelemetry | APM (Application Performance Monitoring) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Vendor-neutral, open-source approach that supports collection of distributed traces, metrics, and logs across cloud-native and microservices environments. | Uses proprietary agents with out-of-the-box instrumentation, focusing on performance data and business transaction insights, but offers limited flexibility in customization. |
| Customization & Flexibility | Highly customizable with modular architecture, supporting a wide range of programming languages and environments. | Pre-configured for ease of use, designed for fast deployment, but with limited flexibility for custom telemetry or configurations. |
| Focus Area | Prioritizes telemetry data across distributed systems, giving visibility into infrastructure, services, and the relationships between them. | Primarily focused on application performance and user experience, offering deep insights into software responsiveness and business transaction tracing. |
| Scalability | Built to handle cloud-native architectures and complex distributed systems, allowing for fine-tuned telemetry collection at large scale. | Scalability varies by vendor; some may struggle in highly distributed environments due to limitations in data collection agents or integration points. |
| Cost Structure | Open-source with no core licensing fees, though additional costs may arise for data storage, processing, and custom analysis tools. | Typically involves licensing fees based on infrastructure size (hosts, instances, etc.), with costs escalating as the application grows or more features are required. |
| Ease of Use | Requires a steeper learning curve, more setup, and technical expertise to configure properly, but offers greater long-term flexibility and control. | Offers quick and easy deployment with built-in dashboards and alerts, making it ideal for teams with limited time or expertise in observability setup. |
| Vendor Lock-In | Avoids vendor lock-in, as it integrates easily with various backend systems and supports open standards, promoting tool interoperability. | Often locks users into specific vendor ecosystems, making it harder to switch solutions without incurring significant migration costs or effort. |
| Ideal Use Cases | Ideal for modern cloud-native applications with distributed architectures, requiring deep observability, customization, and scalability. | Best suited for traditional monolithic applications or businesses seeking fast deployment with minimal setup, often in more legacy or static environments. |
Use Cases: When to Choose OpenTelemetry vs APM
Choosing between OpenTelemetry and APM depends on your organization’s needs, infrastructure, and long-term goals. While both tools serve the purpose of monitoring and observability, their differences make each suitable for specific use cases.
Understanding when to choose one over the other or when to use them together can significantly impact your monitoring strategy’s effectiveness.
OpenTelemetry excels in:
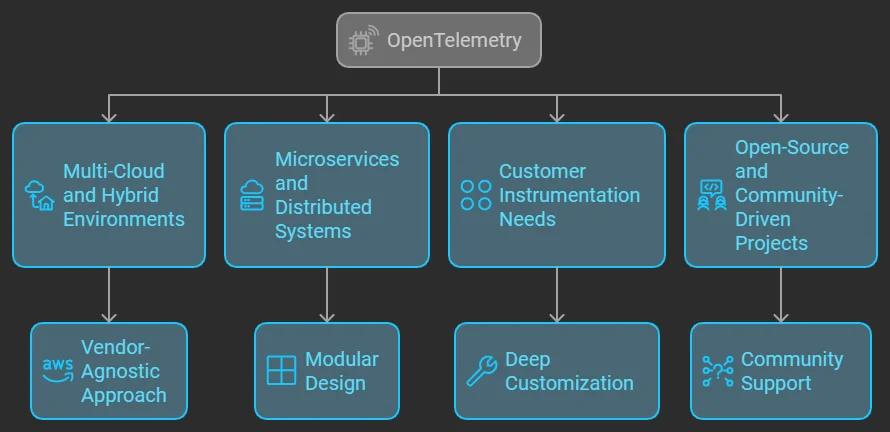
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments: OpenTelemetry is designed with flexibility in mind, allowing seamless integration across multiple cloud providers and hybrid infrastructures.
- Its vendor-agnostic approach ensures consistent data collection and observability, no matter the environment.
- Microservices and Distributed Systems: in highly distributed, cloud-native architectures like microservices, OpenTelemetry’s modular design is ideal.
- It captures granular traces, metrics, and logs across complex, dynamic systems, providing full visibility into distributed transactions.
- Customer Instrumentation Needs: For organizations that demand tailored observability, OpenTelemetry’s flexibility allows for deep customization.
- Developers can instrument specific metrics and traces, ensuring the monitoring solution adapts to unique business needs and evolving architectures.
- Open-Source and Community-Driven Projects: If your organization prioritizes open standards, transparency, and community-driven innovation, OpenTelemetry offers cutting-edge, rapidly evolving features and broad ecosystem support.
When APM Shines:
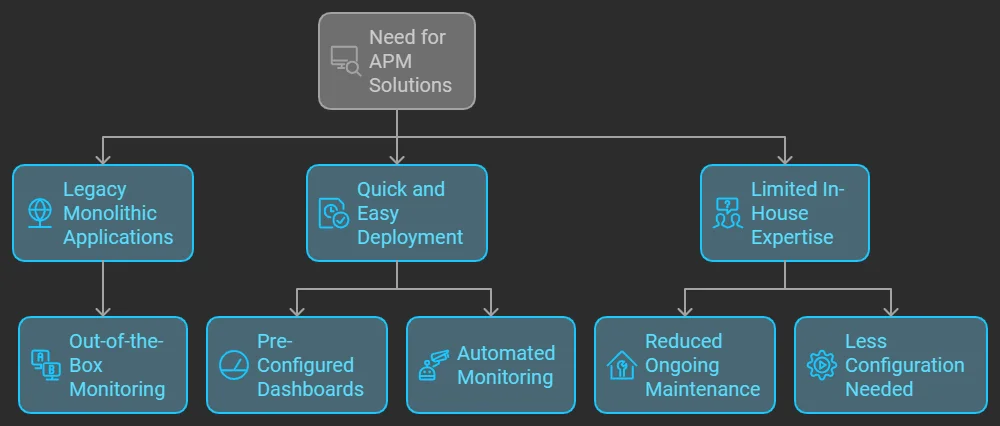
- Legacy Monolithic Applications: In stable, monolithic environments, traditional APM tools excel.
- These applications often require out-of-the-box monitoring, and APM provides ready-made solutions that offer immediate insights with minimal setup.
- Quick and Easy Deployment: For teams under time constraints or without extensive DevOps expertise, APM solutions deliver pre-configured dashboards, automated monitoring, and actionable insights right out of the box.
- This enables faster time-to-value, critical for teams needing rapid observability without extensive custom setup.
- Limited In-House Expertise: For organizations that don’t have specialized monitoring or development teams, APM is an excellent fit.
- The plug-and-play nature of APM solutions reduces the need for ongoing maintenance, configuration, or technical deep drives, making it a straightforward option for less technically adept teams.
Why a Hybrid Might Be Best:
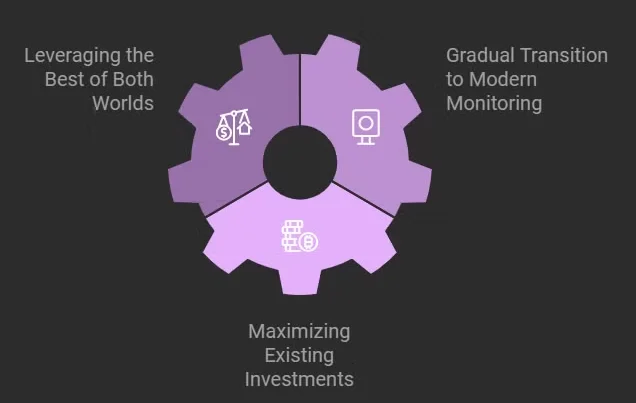
- Leveraging the Best of Both Worlds: Many organizations find that a hybrid approach allows them to enjoy the strengths of both solutions.
- By using OpenTelemetry for flexible and custom data collection, and combining it with APM’s powerful analytics and visualization features, teams can ensure comprehensive observability across both modern and legacy systems.
- Gradual Transition to Modern Monitoring: Teams looking to modernize their monitoring stack can begin by adopting OpenTelemtry incrementally, while still benefiting from the out-of-the-box insights of APM.
- This gradual approach helps balance immediate monitoring needs with a long-term strategy toward open standards and greater flexibility.
- Maximizing Existing Investments: For organizations heavily invested in APM tools but eager to avoid vendor lock-in to adopt new technologies, integrating OpenTelemetry can enhance data collection while maintaining the familiar analytics dashboards and workflows of APM solutions.
The Future of Monitoring: OpenTelemetry and APM Convergence
As the observability landscape evolves, the distinctions between OpenTelemetry and APM are becoming less pronounced. The future of monitoring is heading towards a convergence of both technologies, driven by the following key trends:
- Unified observability platforms: The future is moving toward integrated observability that combines the flexibility and open standards of OpenTelemetry with the robust analytics and ease of use that APM tools offer.
- These unified platforms will allow organizations to collect telemetry data in a vendor-neutral way, while still leveraging sophisticated, pre-built dashboards, alerting systems, and data visualization tools.
- By blending the strengths of both, organizations can have full control over their data pipelines and instrumentation while enjoying turnkey solutions for analysis and reporting, bridging the gap between customizability and usability.
- Advanced correlation and analysis: Modern platforms are evolving to provide deeper, more meaningful insights by correlating data from multiple telemetry sources such as metrics, logs, traces, and events into a single cohesive view.
- These platforms will enable a holistic understanding of system health, user experience, and root cause analysis, breaking down silos between different types of telemetry data.
- The convergence of OpenTelemetry and APM will also allow for improved context-aware analysis, helping teams identify not just the symptoms of issues but also the underlying causes faster and more efficiently.
- AI-powered anomaly detection: Both OpenTelemetry and APM solutions are increasingly leveraging AI and machine learning to enhance monitoring capabilities.
- AI-driven insights transform observability by detecting real-time anomalies, predicting potential failures before they occur, and automatically identifying performance bottlenecks.
- As AI algorithms become more advanced, future monitoring platforms will proactively suggest optimizations, automate root analysis, and even trigger self-healing mechanisms within distributed systems, reducing manual intervention and increasing system reliability.
- Flexible Data Ownership and Vendor-Agnostic Ecosystems: A significant benefit of OpenTelemetry-APM convergence is the shift toward greater data ownership.
- As more platforms embrace open-source standards, organizations will be less reliant on proprietary vendor ecosystems, allowing them to maintain control over their telemetry data.
- This shift will enable greater flexibility in integrating different tools, avoiding vendor lock-in, and ensuring that monitoring solutions can evolve alongside the changing infrastructure and technology landscape.
Implementing OpenTelemetry with SigNoz: A Practical Approach
For those looking to implement OpenTelemetry effortlessly, SigNoz is an excellent open-source APM tool built natively to support OpenTelemetry. It provides full-stack observability for distributed systems with minimal configuration, making it an ideal choice for organizations aiming to adopt OpenTelemetry quickly.
Why Choose SigNoz?
- Comprehensive Observability: Track traces, metrics, and logs across your entire application stack for better insights.
- Native OpenTelemetry Integration: SigNoz seamlessly collects data through OpenTelemetry, simplifying the monitoring process.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Offers both cloud-hosted and open-source models, providing a cost-effective solution based on your specific needs.
To get started with OpenTelemetry and SigNoz, check out this Complete guide on Implementing OpenTelemetry with SigNoz, where you’ll find detailed instructions and tips to optimize your observability setup.
SigNoz cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 19,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- OpenTelemetry provides flexibility and customization, ideal for organizations with diverse or cloud-native environments.
- APM offers out-of-the-box performance insights and analytics, often with advanced AI-driven insights.
- Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid approaches to benefit from the strengths of both OpenTelemetry and APM.
- The future of monitoring lies in openness and interoperability, with OpenTelemetry and APM tools playing crucial roles.
FAQs
Can OpenTelemetry completely replace traditional APM solutions?
- Not entirely, OpenTelemetry excels at collecting and standardizing telemetry data (metrics, logs, traces) across various platforms, but it lacks the advanced analytics, visualization, and out-of-the-box features that traditional APM tools offer.
- Many organizations still rely on APM for pre-built dashboards, automated insights, and ease of deployment, especially when don’t have the resources to build and maintain custom solutions.
- OpenTelemetry can complement APM but may not fully replace it, especially in environments that benefit from the robust features of APM solutions.
What are the main challenges in adopting OpenTelemetry?
OpenTelemetry adoption can present several challenges:
- Initial setup and configuration complexity: Setting up OpenTelemetry requires more manual effort than traditional APM tools, including configuring various components like instrumentation libraries, collectors, and exporters.
- Integrating OpenTelemetry with existing monitoring infrastructure: While OpenTelemetry is designed for modern cloud-native environments, integrating it with older or monitoring applications can be difficult, requiring custom solutions.
- Telemetry Data Quality: Ensuring consistent and high-quality telemetry data across distributed systems, microservices, or hybrid environments can be complex and may require additional resources and expertise.
How does OpenTelemetry impact the total cost of ownership for monitoring?
OpenTelemetry’s open-source nature can reduce upfront software costs, as there are no licensing fees. However, organizations should account for additional costs related to:
- Training: Teams may need to invest time and resources in learning how to set up and use OpenTelemetry effectively.
- Custom Solutions: Since OpenTelemetry requires more manual configuration, organizations may need to spend resources on custom integrations, instrumentation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Data Storage: While OpenTelemetry is free, collecting and storing large amounts of telemetry data 9metrics, traces, logs) can incur significant storage costs, especially when using cloud-based storage solutions.
Is it possible to use OpenTelemetry with existing APM tools?
Yes, OpenTelemetry can be integrated with many APM tools. Most modern APM platforms have added support for OpenTelemetry, allowing organizations to collect data while benefiting from the analytical and visualization capabilities of their existing APM solutions.
- This integration allows for a flexible and comprehensive monitoring strategy, combining OpenTelemetry’s open-source, vendor-neutral telemetry collection with APM’s advanced features for performance monitoring and troubleshooting.